Controller Manager
Proposal A - fully configurable, most flexible
Configuration
- Each controller manager instance (process) has the following fields:
- Type: specifies the default launch configuration, including which controller it will start and how many workers the controllers will have
- Id: instance type
- Implementation location: new data type in storage (config map is watched by all nodes. This design has health probe data and will be updated frequently. Not suitable for config map.)
ControllerManagerDefault:
- controller-manager-type: pods
controllers:
- type: deployment
workers: 5
- type: scaleset
workers: 10
- controller-manager-type: jobs
controllers:
- type: job
workers: 5
- type: cron-job
workers: 5
ControllerManagerInstances:
- controller-manager-id: uuid1
controller-manager-type: pods
last-healthprobe-at: '2019-05-01 01:00:00'
is-alive: true
controllers:
- type: deployment
workers: 5
- type: scaleset
workers: 2
- controller-manager-id: uuid2
controller-manager-type: jobs
last-healthprobe-at: '2019-05-01 01:00:00'
is-alive: true
controllers:
- type: job
workers: 8
- type: cron-job
workers: 2
Start & Update Workflow
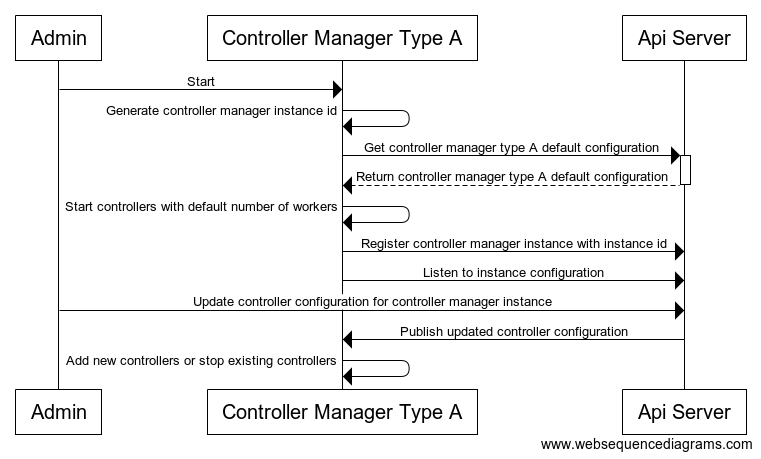
Proposal B - All controller runs in each controller manager, with fixed # of workers configured
Configuration
- All controller runs in each controller manager, with fixed # of workers configured
- When there is missing configuration for a controller, default to worker 1
- Change of configration only affects newly started controller manager, existing controller managers won't be affected
- Implementation location: config map
ControllerManager:
- controllers:
- type: deployment
workers: 5
- type: scaleset
workers: 10
- type: job
workers: 5
- type: cron-job
workers: 5
Controller
Unsupervised Workload Distribution
Solution A - Balanced workload distribution
Ideas
- Any consistent hash function
- Upon controller start, get full set of workloads that are not completed. (Need to check workload state support)
- Internal records of all none completed workloads with minimized attributes: workload id, namespace/name (cache key), created timestamp, status, current assigned controller instance id
- Map of workload id -> workload record
- Map of controller instance id -> set of workloads
- Upon update of instances, recaculate workload ownership; for affected workloads, reassign
- Need algorithm to find delta
Problems and Analysis
- Affected workloads need to be reread for status update
- Unavoidable for any reassignments
- How to avoid massive traffic and recalculation caused by workload reassignment?
- If controller instance updates happen frequently, there will be a lot of reassignment
- Reread and increased traffic increment/recalculation cannot be avoid but can be distributed throughout the processing period
- Memory usage for all workload storage
- Minimize workload data saved in memory
- Need to estimate and performance test for the benchmark
- Can controller be locked for a very long time when system is not stable?
- Lock controller means there will be no processing of new workload. It does not block new controller registration or removal. Once controller instances are stabilized, it will resume processing workloads.
- Performance test need to simulate this scenario
- Workloads are watched by all controller instances, network traffic and request on api/core server is multiplied
- Minimize workload traffic by introducing minimized workload data type and watch minimized workload data type from api/core server
- For related workload (such as pod for replicaset), filter out the ones that do not have owner references
Solution Overview
- Using consistent hash to distribute workload to multiple controller instances
- Consistent hash is used to make sure workloads are evenly distributed, also minimize the impact of controller instance updates on workload redistribution
- Internal memory to cache all minimalized workloads
- Facilitate fast workload redistribution
- Controllers are centrally registered
Controller Instance Registry in Storage
- A. Add the entire data controller instance structure into storage
- A shared controller lock for add/remove controller instances
- Lock is only for controller instances adjustment, not for workload distribution or redistribution
Controllers:
- controller-type: VirtualMachine
locked: false
instances:
- instance-id: uuid1
last-healthprobe-at: '2019-05-01 01:00:00'
- instance-id: uuid2
last-healthprobe-at: '2019-05-01 01:00:00'
- instance-id: uuid5
last-healthprobe-at: '2019-05-01 01:00:00'
- controller-type: BareMetal
locked: true
instances:
- instance-id: uuid3
last-healthprobe-at: '2019-05-01 01:00:00'
- instance-id: uuid4
last-healthprobe-at: '2019-05-01 01:00:00'
- B. Use etcd lease and timeout mechanism
- When a new controller starts or rejoin the network, it will renew its key with storage and attach a timeout
- If a controller is in the list, it is alive; otherwise, it is out of the loop
Controllers:
- VirtualMachine
- <instance-id-v1>
- <instance-id-v2>
...
- <instance-id-vm>
- BareMetal
- <instance-id-b1>
- <instance-id-b2>
...
- <instance-id-bn>
| Solution | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| A |
|
|
| B |
|
|
- Suggestion: phase I take solution B. Migrate to solution A if migration is necessary.
Controller Internal Data Structure
- Workload data structure
- Workload id, name, namespace, controller instance id, created timestamp, status, optional workload details
- Memory usage estimation:
- 8 (uuid) + 20 (name) + 20 (namespace) + 8 (uuid) + 24 timestamp + 100 (status) = 180 bytes
- 1M bytes ~= 5K workloads, 0.3M workloads ~= 60M bytes memory usage (ok)
- Map of controller instance id to set of workload ids
- Use for distributed workload ownership calculation
- Map of workload id to workload
Controller Internal Workflow
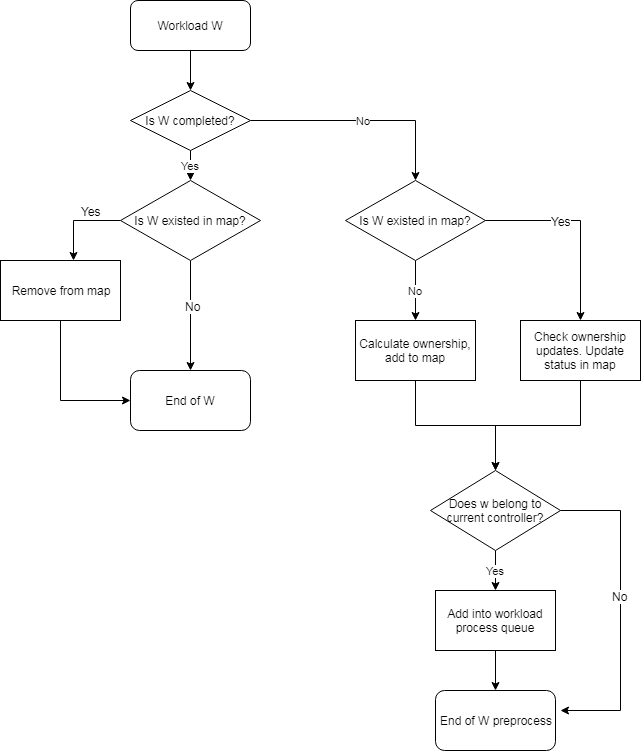
Preprocess of Workflow - single controller
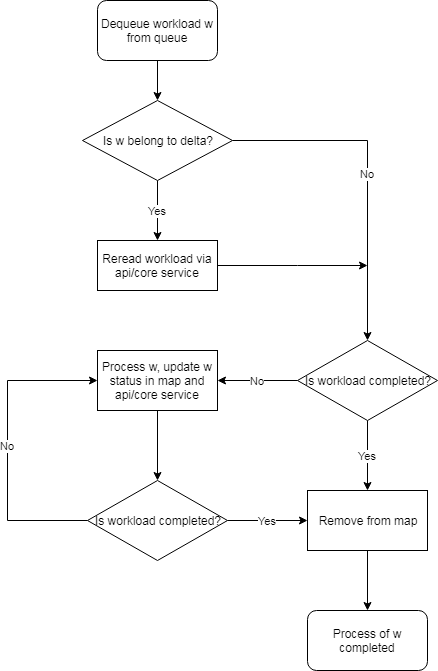
Process of Workflow - single controller
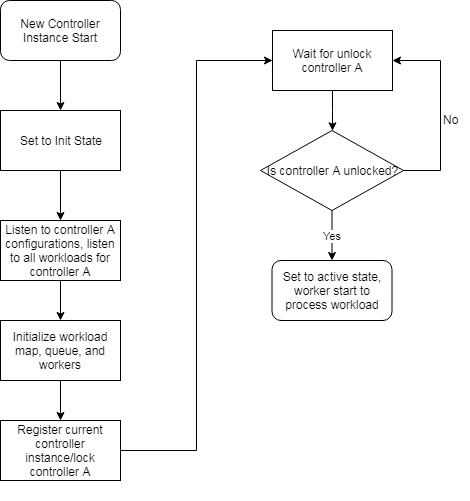
Controller Instance CUD
Controller Instance Initialization, Update/Delete
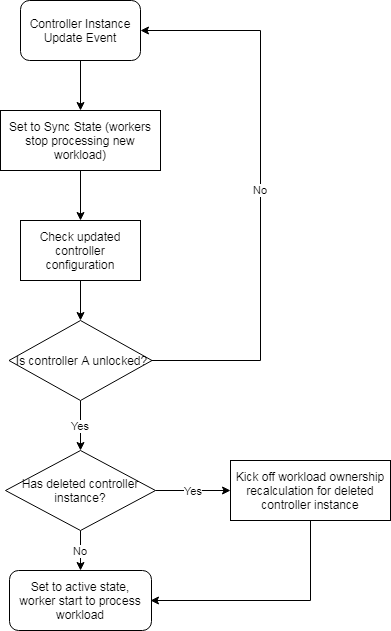
Controller Instance Synchronization
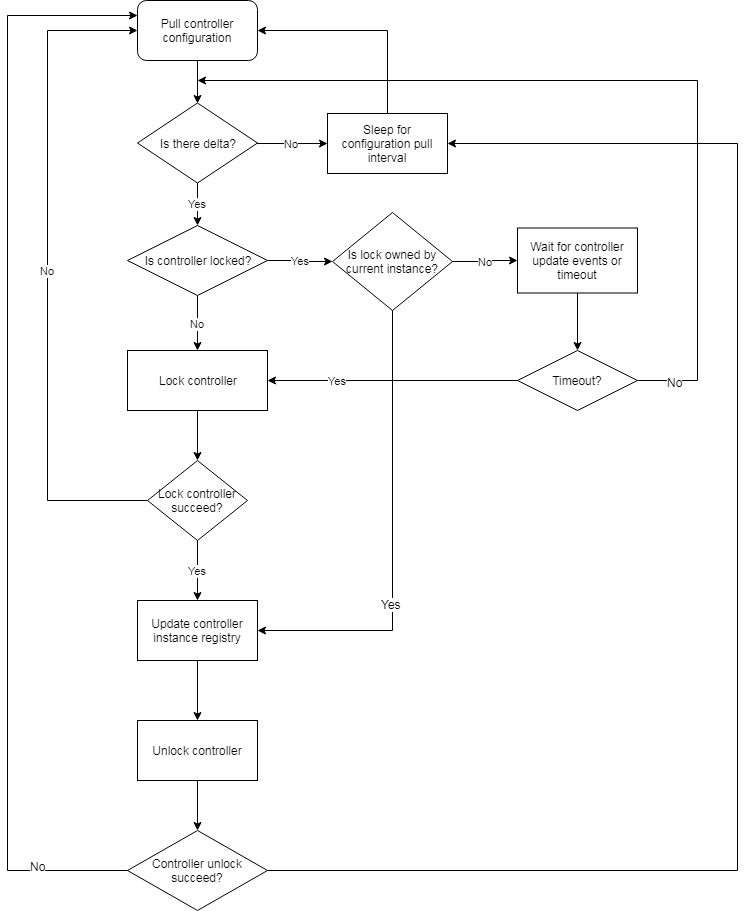
Algorithm
. Consistent hashing algorithm: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stathat/consistent/master/consistent.go